Git integration
Git is a free and open source distributed version control system designed to handle everything from small to very large projects with speed and efficiency.
Experienced git users may prefer to use Terminal. That option is always available alongside the UI version. The easier version for most users is the UI version (jupyterlab-git). Follow instructions below on how to use UI version. To learn more about git, go to https://git-scm.com
Git Clone
To start working with remote git repository, you first need to clone it to JupyterLab. In the file manager, click on the ‘Git Clone’ button, as shown below
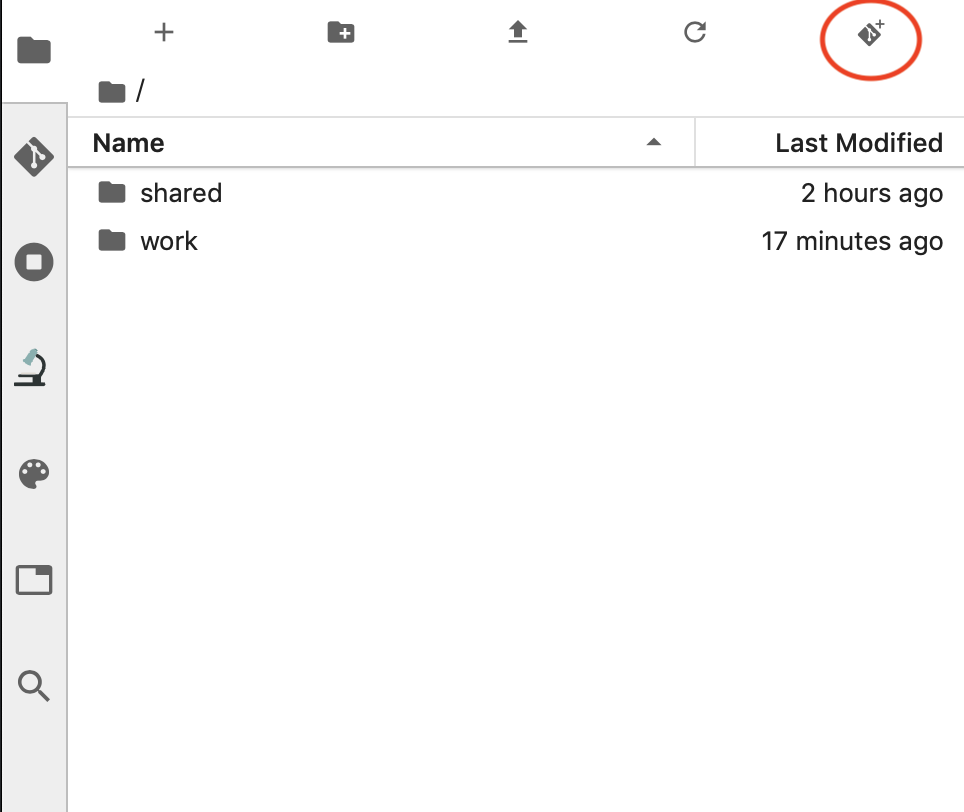
git_1
In the dialog, that opens after that, type or paste the link to your git repository. For example, if hosted on GitHub, click the green ‘Clone or download’ button and then copy the url to paste it to the form.
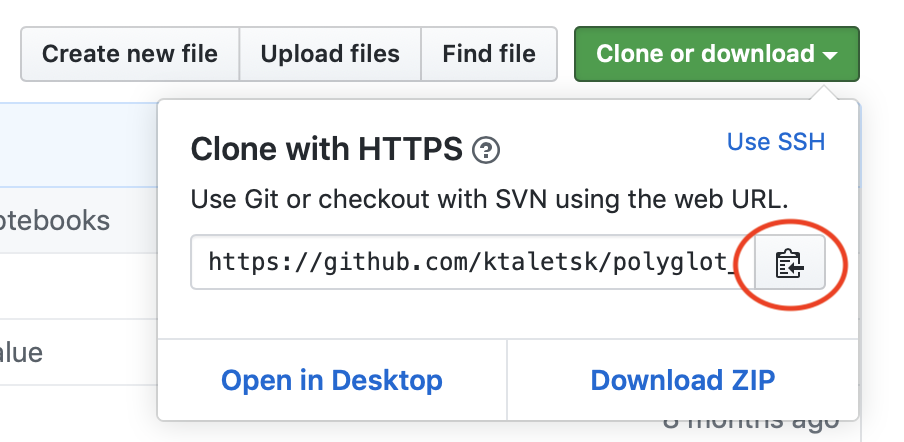
git_2
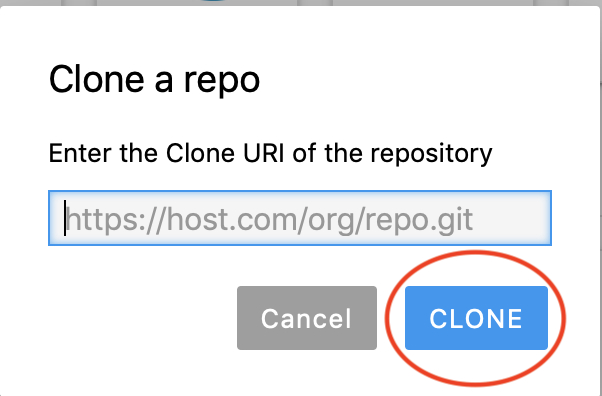
git_2
If the repository you are trying to clone is in the private repository, you will be prompted to enter your credentials:
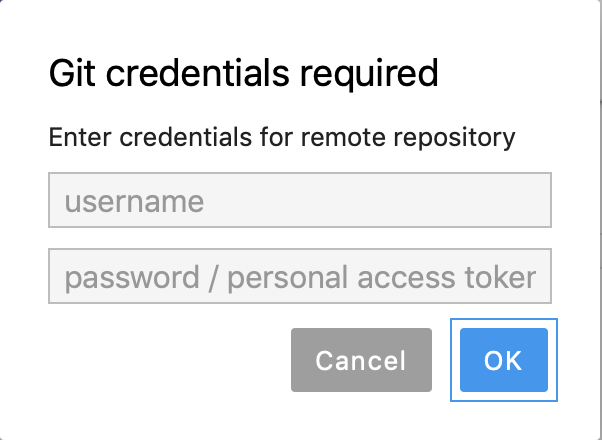
git_3
Git Commit
After you make some changes to your git repository, you may want to save your work and/or share with others. To do that, you need to first commit your changes to git.
See changes in the notebook
To see the latest diff (new changes since the last commit), click
‘git’ button in the top bar as shown below:

git_4
You will see the output similar to one shown below:
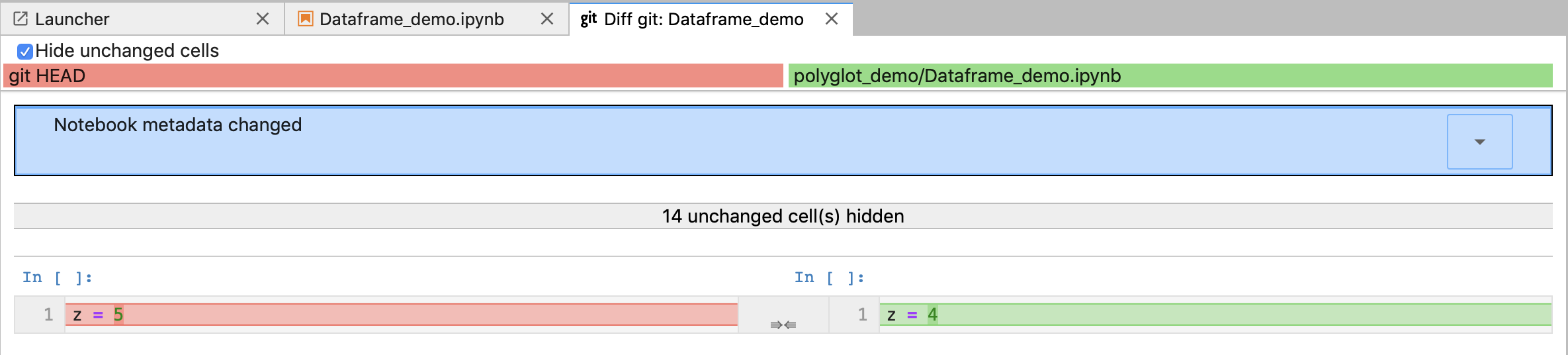
git_5
Previous version is shown in red on the left and the latest version is shown in green on the right
Commit changes
Click git tab in the left panel to see the list of files that have changed since the last commit
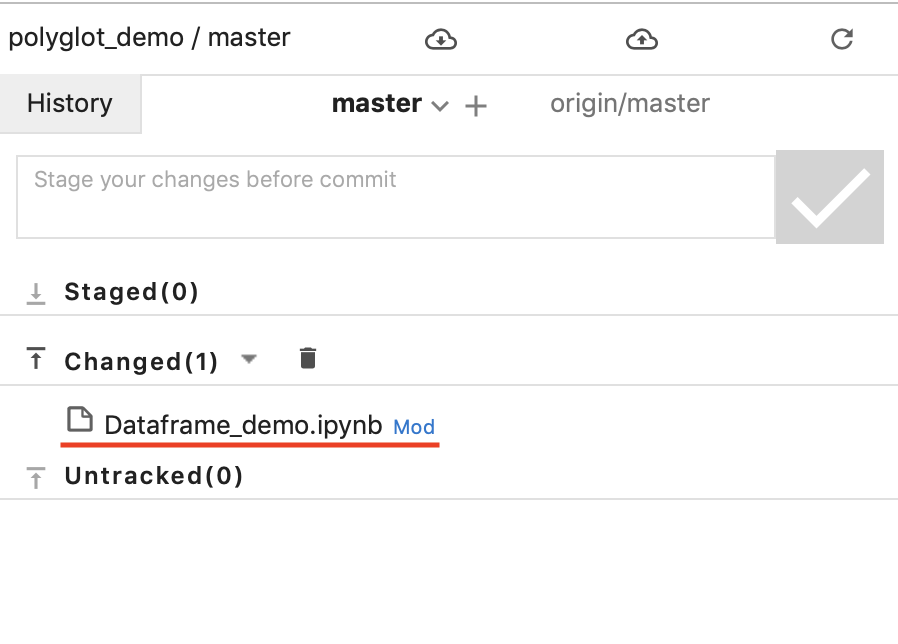
git_6
Click the arrow up button to add the file to a staging area for new commit or click trash bin button to discard changes on that file
Once you have all the files you want to stage for a new commit, type the commit message in the input field on top of the panel. After that click blue checkmark button to create a commit.
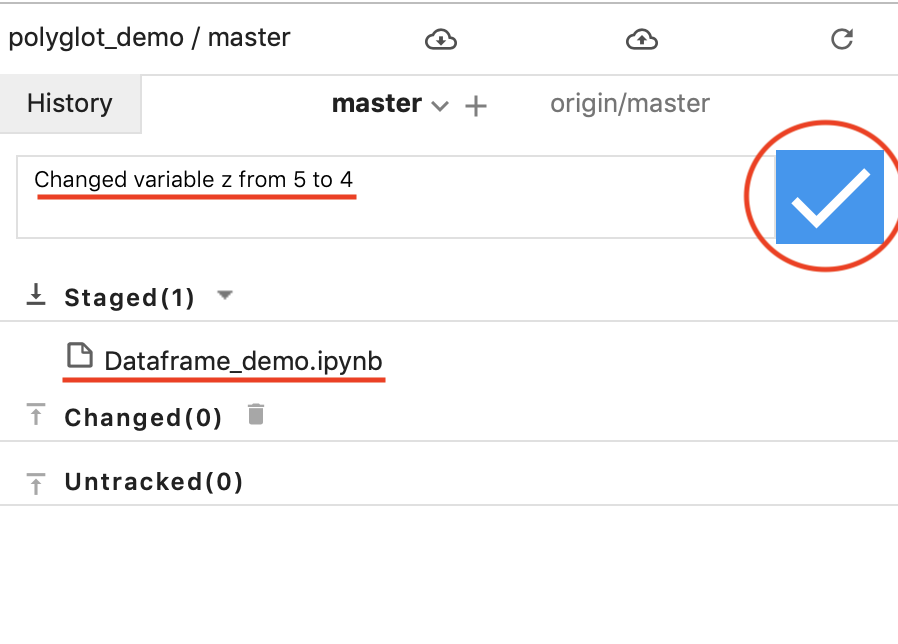
git_7
If you are commiting for the first time, you would be asked to type in your name and email. If commiting to Gihub, use the same name and email that you have on Github to properly attribute your commit to you.
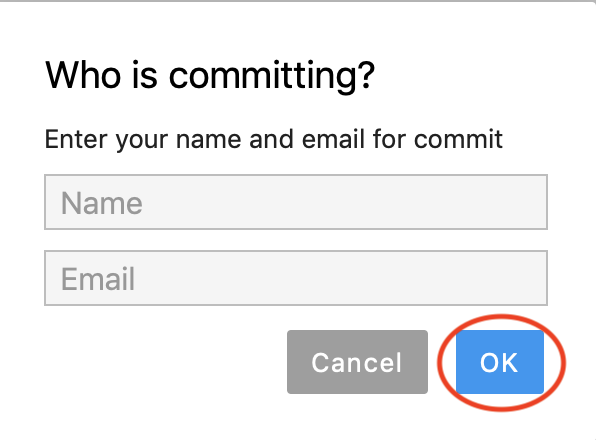
git_8
Push commit
Finally, push commit to remote repository. You will be asked to type your login and password.
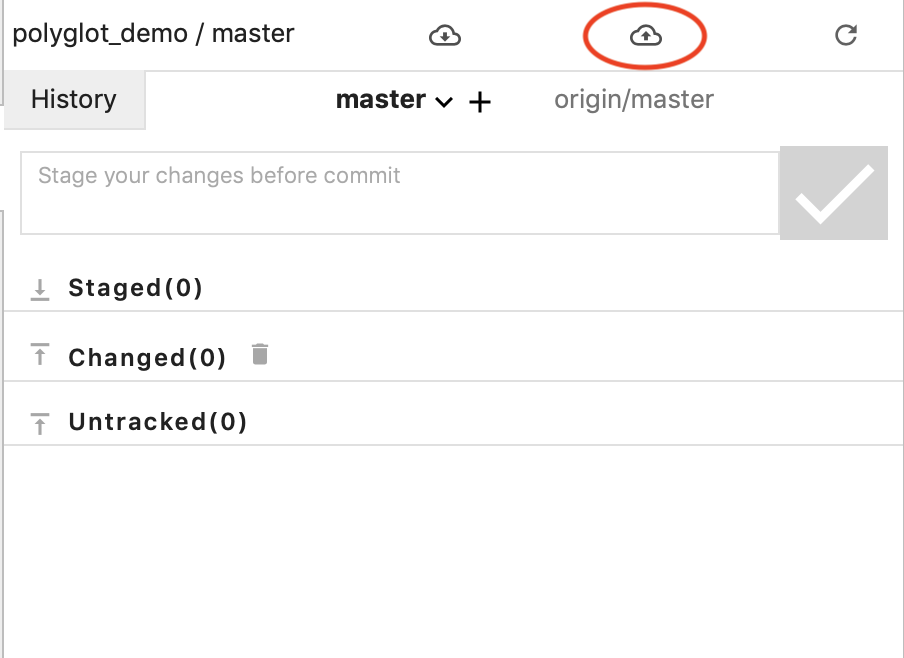
git_9